The football league is in full swing, with players speeding across the green field. The goalkeeper repeatedly blocks off the threats. In the world of electronic components, a silent "defensive battle" is also unfolding. Anti-static packaging is acting as a "goalkeeper", blocking off the invisible "static assassins". This unseen contest is crucial to the survival of precision electronic equipment.
Where Does Static Electricity Come From��?
Static electricity is not a product of modern technology; rather, it is a common physical phenomenon in nature. When two different materials come into contact and then separate, or when the humidity in the environment is too low, electrons will transfer, causing static charges to form on the surface of the objects. In daily life, the crackling sound when taking off a sweater, or the stinging sensation when touching a metal handle to open a door, are all manifestations of static electricity release. In the field of electronic manufacturing, the human body, equipment, packaging materials, and even air flow can all be sources of static electricity generation.
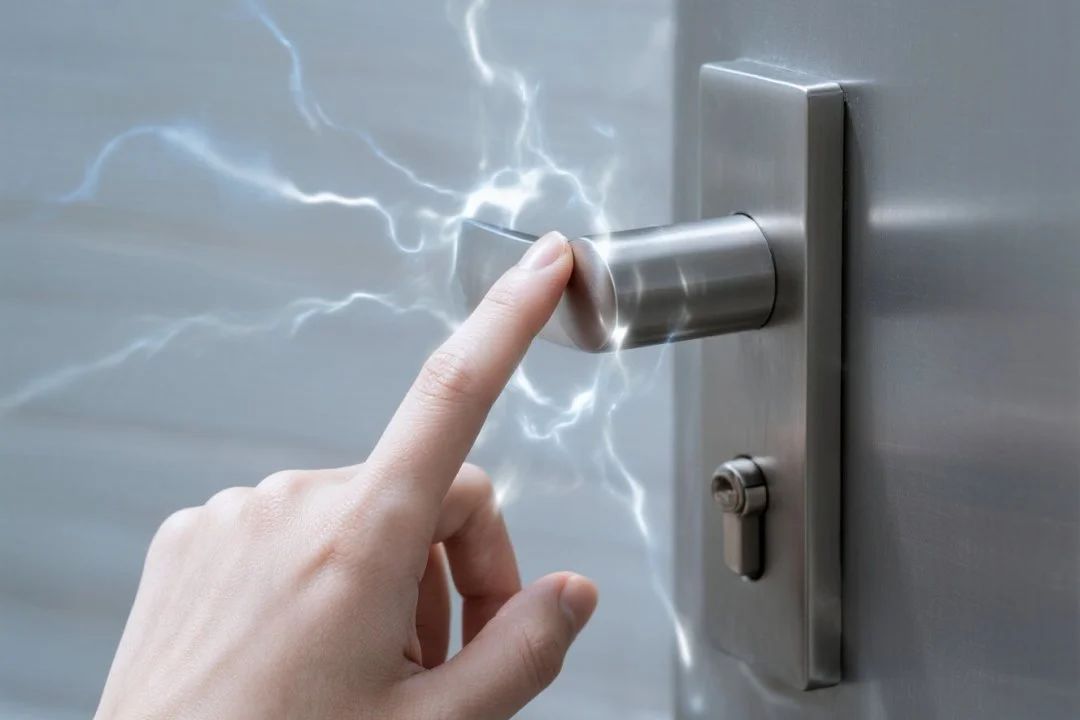

Hazards of Static Electricity
For precision components such as semiconductor chips and PCB circuit boards, static electricity can be regarded as a "hidden killer". The static electricity carried by the human body may seem insignificant, but it can generate an electric arc upon contact with the components, breaking through the oxide layer that is only a few micrometers thick. According to statistics, the global electronics manufacturing industry suffers losses of up to several billion dollars each year due to static electricity damage. Moreover, some damaged components do not immediately fail but gradually lose their functionality during use, ultimately leading to an increase in the failure rate of consumer devices.
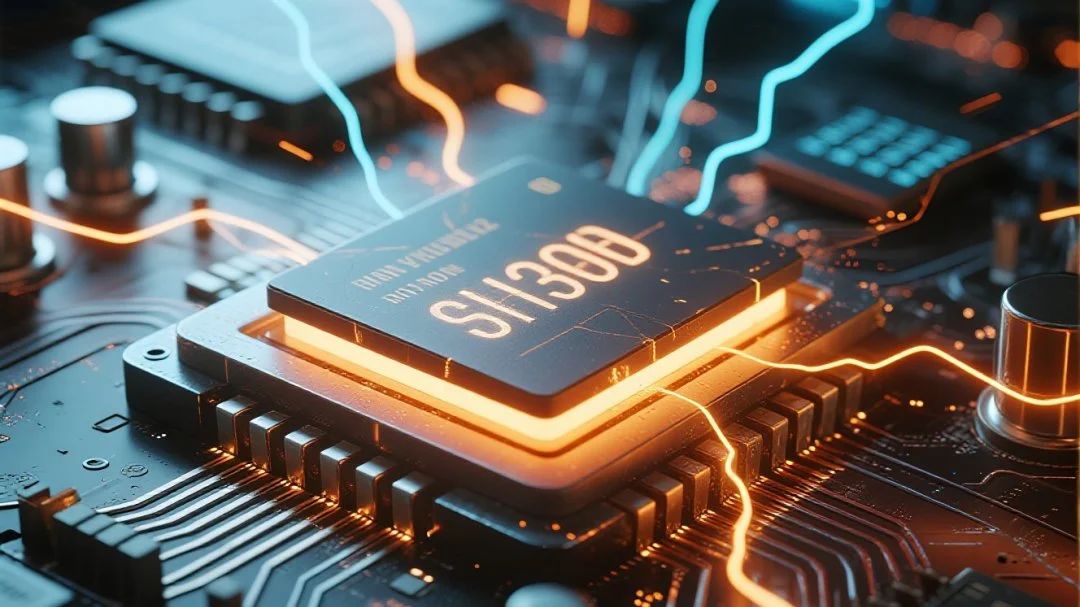
How to Be a Good Goalkeeper
The "defense strategy" for anti-static packaging can be divided into three main aspects:
1. Electromagnetic shielding: The outer layer is made of metal foil or conductive composite materials to form a "Faraday cage", which blocks external static fields and prevents them from affecting the internal items.
2. Anti-static: By adding anti-static agents, the friction voltage is reduced, and static electricity generation is inhibited through friction.
3. Static dissipation: Using dissipation materials with surface resistances ranging from 10^4 to 10^11 Ω, the static electricity is released slowly to avoid instantaneous discharge that could damage components.
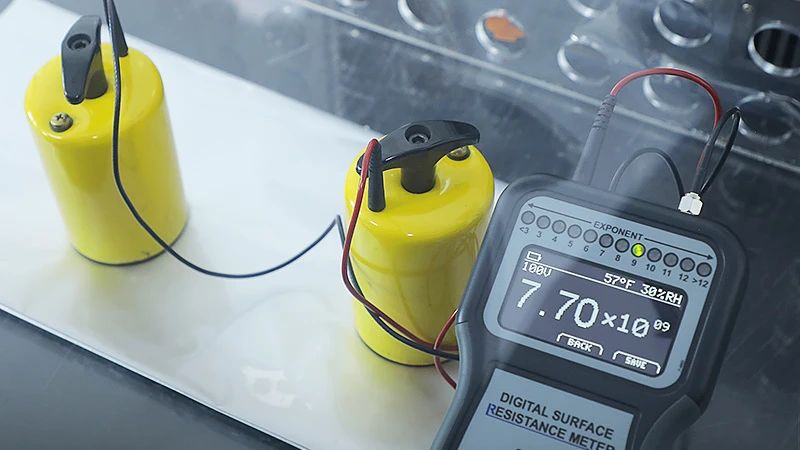

Who is the "Best Goalkeeper"?
There are two main types of "goalkeepers" in the market:
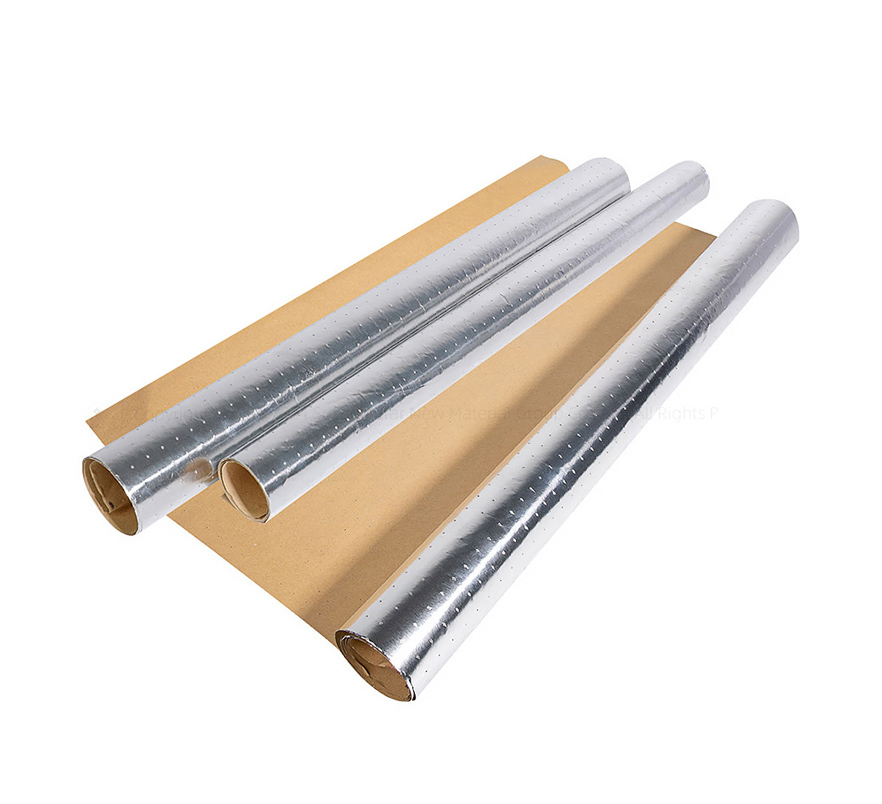
Aluminum foil bags: They adopt a three-layer or four-layer structure of PET (BOPP)/AL/(NY)/CPE, featuring excellent barrier properties, moisture-proof, oxygen-blocking, corrosion prevention, anti-static, high puncture resistance, good light-blocking performance, etc. They are suitable for communication and aerospace components, high-precision mechanical parts that are extremely sensitive to static electricity.
Shielding bags: They adopt a double-layer structure of APET + CPP (CPE), balancing shielding effect and cost advantages. They are suitable for electronic products that are relatively sensitive to static electricity, such as PCB boards, hard drives, memory/flash memory, optical/electro-optical, 5G communication, LED chips, IC semiconductors, and microelectronic components.
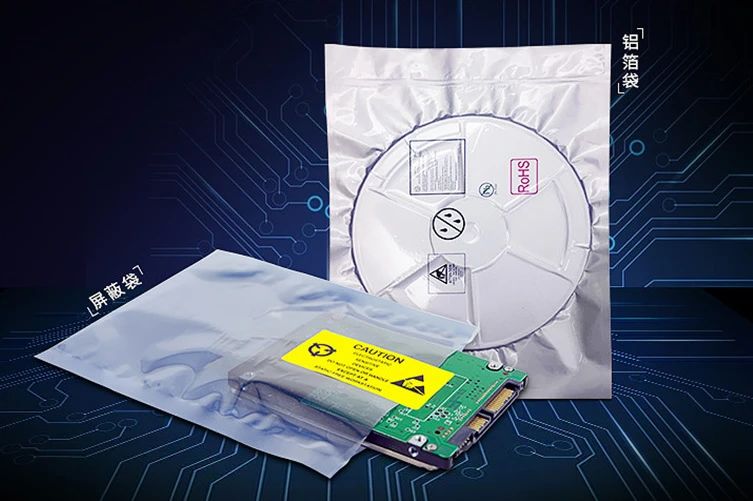

The two are like different styles of goalkeepers on a football field: The aluminium foil bag is the "savior" that focuses on crucial matches, while the shielding bag is the "best value" choice for regular games.
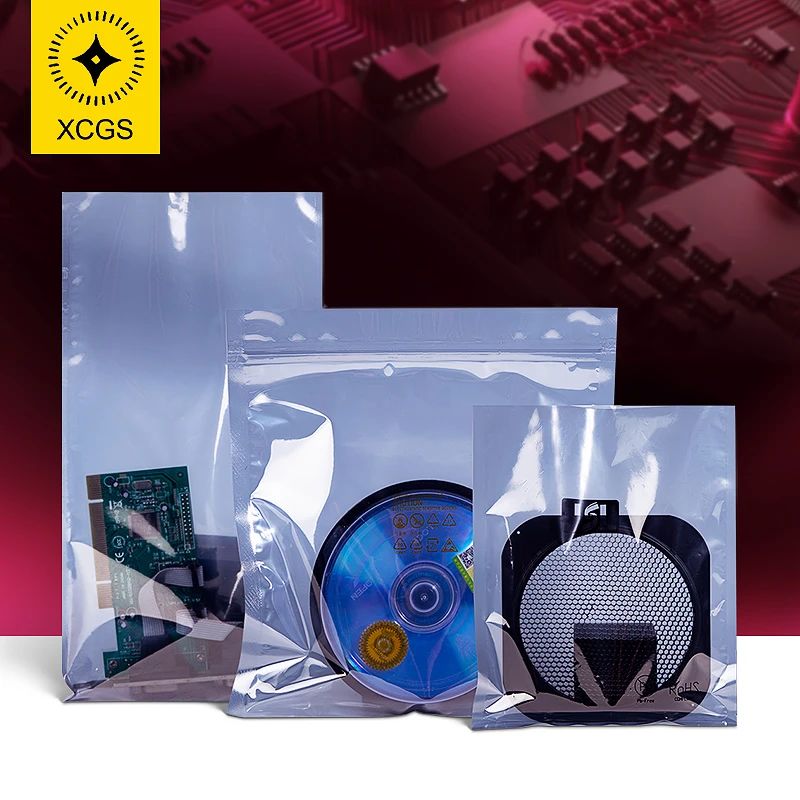


In the silent arena of electronic components, anti-static bags are the most reliable "gatekeepers". Select the right anti-static bag to purchase a "safety insurance" for your precision components. When buying anti-static bags, please trust XCGS!







































































































 18915559236
18915559236 xcbxa@xcgs.com
xcbxa@xcgs.com